This is part 2 of our Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning series. In part 1, we explored the basics—the definitions, how machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence, and the major paradigms of machine learning. Let’s understand why AI/ML is important to the supply chain of the future.
Challenges to the Modern Supply Chain
As globalization increases, so do customer expectations, market volatility and the risk of disruptions. These result in more complex supply chains that will be increasingly challenging to manage, especially using traditional or conventional methods. Furthermore, global disruptions such as COVID-19, geopolitical uncertainty and climate change adversely impact our extended supply chains. Not to mention the market pull for constant product innovations and volatile supply and demand that continue to add pressure on companies everywhere. These disruptions are costly to manage; research reveals that companies can expect to lose between 30%–50% of one year’s EBITDA every decade due to severe and prolonged disruptions1.
Even under “normal” circumstances, many companies face challenges in getting their supply chains to run optimally. This largely stems from a lack of end-to-end visibility, agility (to adapt supply chains to changing demands and trends), flexibility (to leverage spare capacity strategically) and collaboration (between internal silos and across the supply chain). Additionally, the reliance on manual processes, legacy technologies, heterogeneous systems, decentralized processes and IT only inhibits efficient planning, resulting in supply chain plans that are disconnected from real-world operations. This exacerbates the challenges for manufacturing and supply chain organizations in addressing competing business goals, and constraints around resources and materials, profitability and sustainability—the last of which is becoming the most critical lever for strategy at the business level*.
The solution to this complex challenge lies in embedding innovation and resilience across the supply chain—from sourcing and production to distribution and sales. This requires a paradigm shift in supply chain design, leveraging advanced digital technologies that supplant traditional ways of working. Through horizontal and vertical integration of the organization, digitalization leverages information not captured, unavailable or unutilized towards eliminating inefficiencies.
Innovation & Resilience: Key to Addressing Modern Supply Chain Challenges
Innovation is not limited to developing new products or supply chain drivers. It additionally encompasses continuous improvement in the way supply chains operate, specifically around the degree of alignment between physical and financial flows, and business processes with information flow. Resilience is the ability of the supply chain to minimize the adverse impact of disruptions while recovering to its original functional state, or better and quicker.
We’ve identified four key drivers of innovation and resilience in supply chains, as illustrated in EXHIBIT 1.
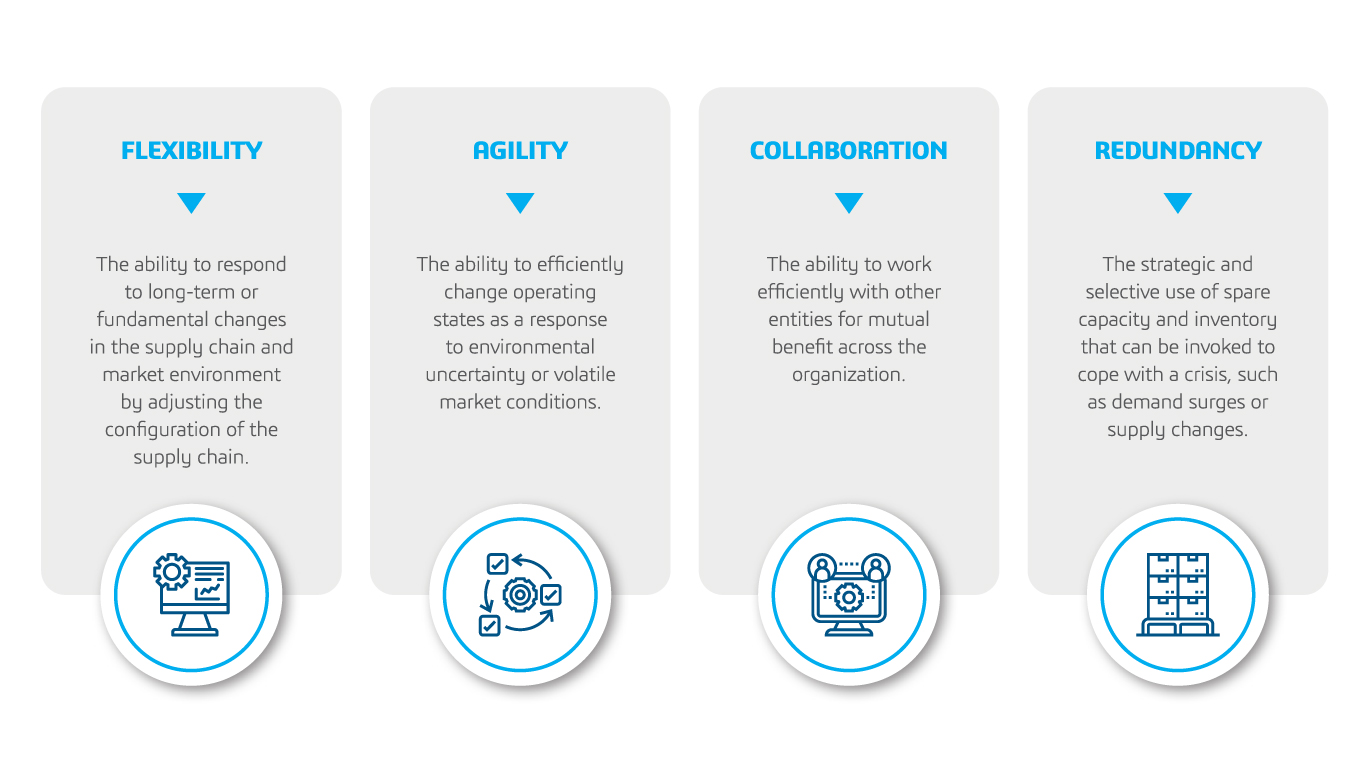
The key drivers of supply chain resilience are:
- Flexibility – the ability to respond to long-term or fundamental changes in the supply chain
- Agility – the ability to efficiently change operating states as a response to environmental uncertainty
- Collaboration – the ability to work efficiently with other entities for mutual benefit across the organization
- Redundancy – the selective use of spare capacity and inventory that can be invoked to cope with a crisis
Digital Technologies like AI, ML, Robotics are Critical Enablers of the Supply Chain of the Future
“Digital” is recording and storing information in an electronic media, such as computer systems, to provide new value-generating opportunities by leveraging data, analytics and allied technologies.
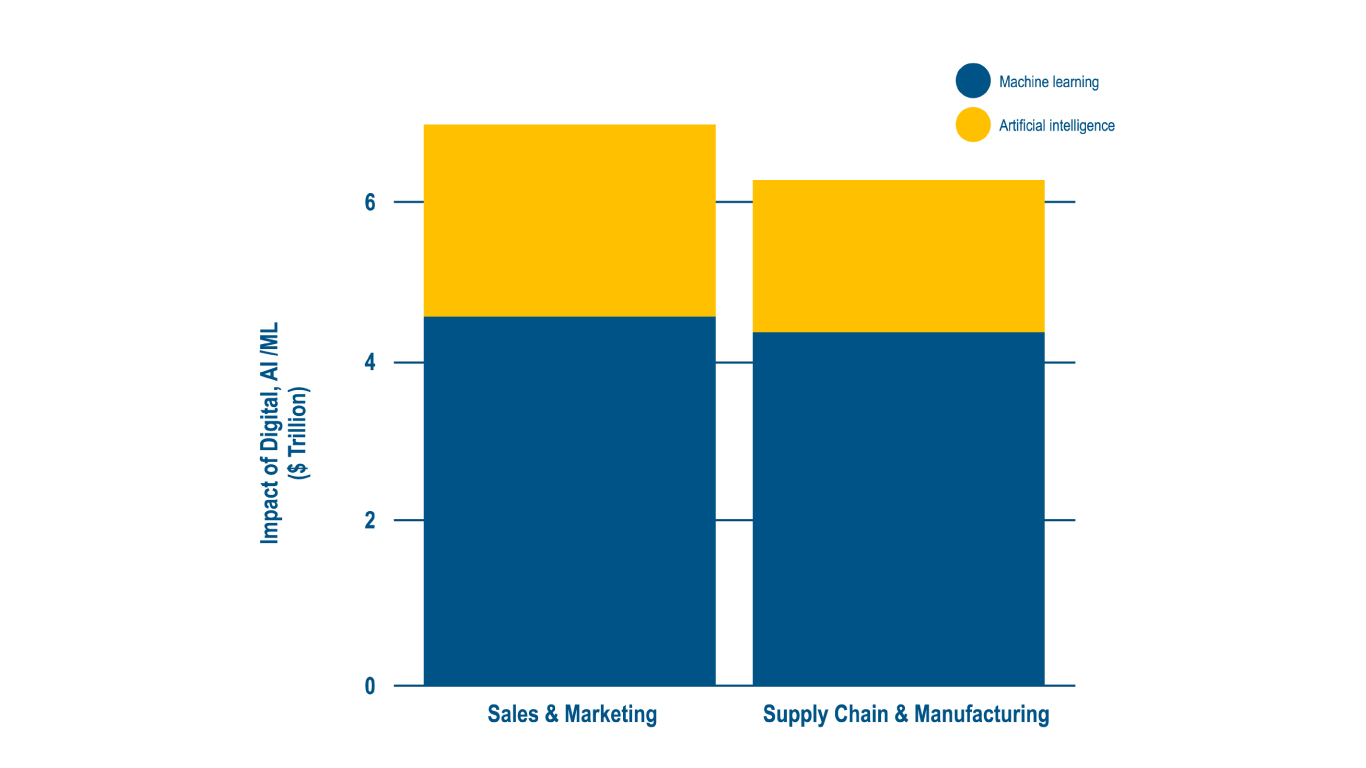
Digitization enables the integration of an organization’s processes, both horizontally; across functional areas, and vertically; across the entire supply chain. This enables real-time visibility throughout the supply chain—from product development and sourcing through manufacturing, distribution and customer service. A spectrum of digital technologies, like digital control towers, analytics, IIoT, AI, ML and robotics, augments real-time visibility with capabilities such as evaluating ‘what-if’ scenarios and assessing trade-offs (e.g. make vs. buy). Such capabilities enable foresight, smart operations and decision automation—helping to unlock the next wave of productivity increase. This is expected to have the highest impact in Sales & Marketing, Supply Chain Management (SCM) and Manufacturing, with the potential for $3.5–$5.8 trillion in SCM and Manufacturing annually, as illustrated in Exhibit 22.
In part 3 of this series, we will explore the DELMIA distinction, i.e. how we are uniquely positioned to help customers leverage the true potential of AI/ML.
References:
- McKinsey & Company. “Risk, resilience, and rebalancing in global value chains” (6 August 2020)
- Chui, Michael; Henke, Nicholas and Miremadi, Mehdi. McKinsey Analytics. “Most of AI’s business uses will be in two areas” (March 2019)
Footnote:
* Increasing customer preference towards lowering environmental footprint has pushed industrial companies to strive for more sustainable operations, rendering sustainability a key part of organizational strategy.
