Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) often used interchangeably, yet they refer to two distinct technologies. While virtual reality is a complete simulation of an artificial environment, augmented reality superimposes virtual elements in the real world. In this article, I will explore the differences between these two technologies.
Focus on Virtual Reality
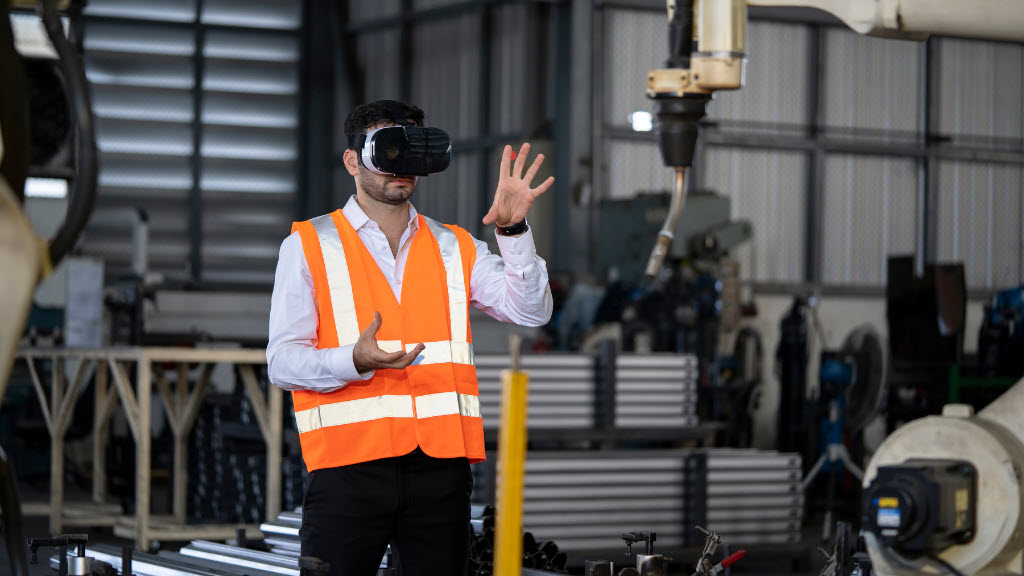
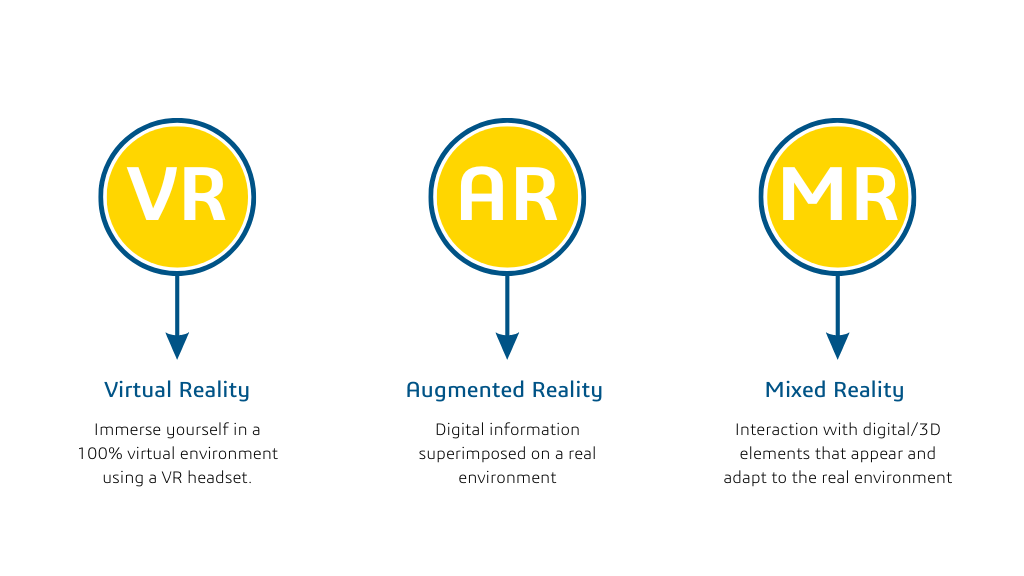
Virtual reality consists in creating an artificial environment in 3D that is fully immersive for the user. Virtual reality headsets contain sensors that track the user’s head movements. They adjust the view in real-time, giving the user an entirely immersive experience in the virtual world.
Headsets are used for a variety of applications, such as video games, professional training, medicine, architecture, and more. Users can interact with virtual objects and move around the environment naturally, which can make the experience very immersive. In industry, VR can simulate work environments for worker training and product design. It can train workers in complex procedures by simulating dangerous or hard-to-reach work environments or improve product design by allowing engineers to visualize virtual prototypes before building them.

What’s Augmented Reality
Conversely, augmented reality uses the camera of a mobile device or headset to superimpose virtual elements in the real world. These elements include images, videos, sounds, or contextual information, such as directions or product data.
Augmented reality is often used in mobile applications for retail, advertising, education, and video games. For example, retail apps can allow customers to virtually view furniture in their own space before purchasing, while educational apps can overlay information about historical landmarks on a sightseeing tour.

Key differences between virtual reality and augmented reality
The main difference between virtual and augmented reality is how users interact with the environment. In virtual reality, the user is fully immersed in a virtual environment, while in augmented reality, the user remains in the real world but with virtual elements overlaid.
Another important difference is the hardware required for each technology. Virtual reality requires a specific headset equipped with sensors to track head movements, while augmented reality can use a simple smartphone or tablet.
And what about mixed reality?
Mixed reality (MR) technology combines augmented and virtual reality elements to create an interactive, immersive environment. Its capabilities enable the identification of both hands and environmental elements such as walls, tables, and obstacles. This adaptation to reality enables virtual content to conform to the environment, establishing a significant difference between mixed, augmented, and virtual reality. MR helps workers perform complex tasks in the industry by providing real-time information about their working environment.
How does it work?
Mixed reality works by using tracking sensors to follow the user’s movements and combining virtual elements with the user’s vision through transparent screens. The sensors detect head and hand movements, enabling users to interact with virtual objects in the mixed environment. Virtual images are superimposed in the real world in real-time, creating an immersive, interactive experience.
The benefits of mixed reality in the industry
Mixed reality offers many possibilities in the industrial sector. It can train technicians by simulating real-life situations and enabling risk-free hands-on training. It can also facilitate product design and modeling, enabling direct interaction with virtual prototypes while learning in a hands-on, immersive way. This capability reduces the risks and costs associated with on-the-job training. Moreover, mixed reality facilitates collaboration between teams, enabling multiple users to share the same virtual experience and interact.
Virtual, mixed, and augmented reality are distinct technologies with different applications. Virtual reality is ideal for fully immersive experiences, while augmented reality is ideal for adding virtual elements to existing experiences. But whichever technology, all three have the potential to transform the way we interact with the digital world and create new opportunities in the industry. By understanding the differences between these technologies, you can choose the one that best suits your needs and delivers immersive, engaging user experiences. Discover our DELMIA Augmented Experience solutions.

