In 1987, the United Nations Brundtland Commission defined sustainability as “meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. Since then, and accelerated by the UN Sustainable Development Goals and the Paris Agreement, sustainability initiatives have moved to the forefront for businesses and governments alike.
One of the key topics for meeting environmental goals is to overcome the greenhouse effect: the threat created by excessive amounts of CO2 that trap the sun’s heat energy in the atmospheric bubble, warming the planet and the oceans. An increase in CO2 plays havoc with the Earth’s climates by causing changes in weather patterns.
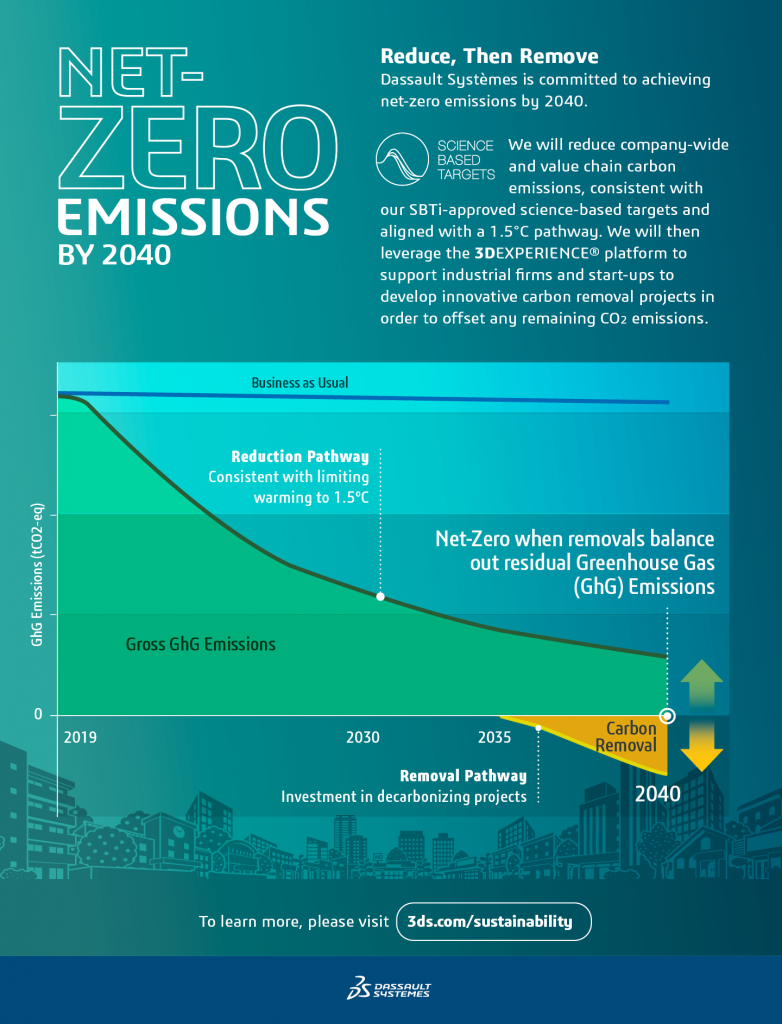
The reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions to lower global warming to a max of 1.5°C can only be achieved with net zero carbon targets. There are similar terms out there that can sometimes cause confusion. For example, the term Carbon Neutral is used when industrial practices still can result in carbon emissions, but there are technologies or processes that can offset these. Net Zero with Science-Based Targets (SBT) means first drastically reducing company-wide and value-chain carbon emissions in line with limiting warming to 1.5°C, and only then balance any remaining emissions by removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Dassault Systèmes believes net zero with SBT is the most credible path forward, in which we drastically reduce emissions and offset the last remaining emissions.
As a world leader in 3D digital technologies, we have furthered our purpose to harmonize product, nature and life by establishing a strategy to reduce emissions in line with climate science, with a goal to reach Net Zero by 2040. Our approach, summarized in the graphic below, prioritizes carbon removal projects supported whenever possible by our sustainable innovation solutions.
For more information: