Introduction to Additive Manufacturing and 3D Printing
In the evolving landscape of manufacturing, Dassault Systèmes is at the forefront, leveraging advanced technologies to revolutionize how products are designed, simulated, and produced. Additive manufacturing, often synonymous with 3D printing, is a pivotal innovation in this realm. While the terms are frequently used interchangeably, additive manufacturing typically denotes professional-level applications involving sophisticated methods such as metal powder bed fusion, material deposition, or electron beam melting. Conversely, 3D printing is often associated with consumer-level applications using plastic printers. Dassault Systèmes focuses on the former, emphasizing professional-grade solutions that facilitate the creation of complex structures and components across various industries.
SIMULIA and DELMIA: Comparison and Complementarity
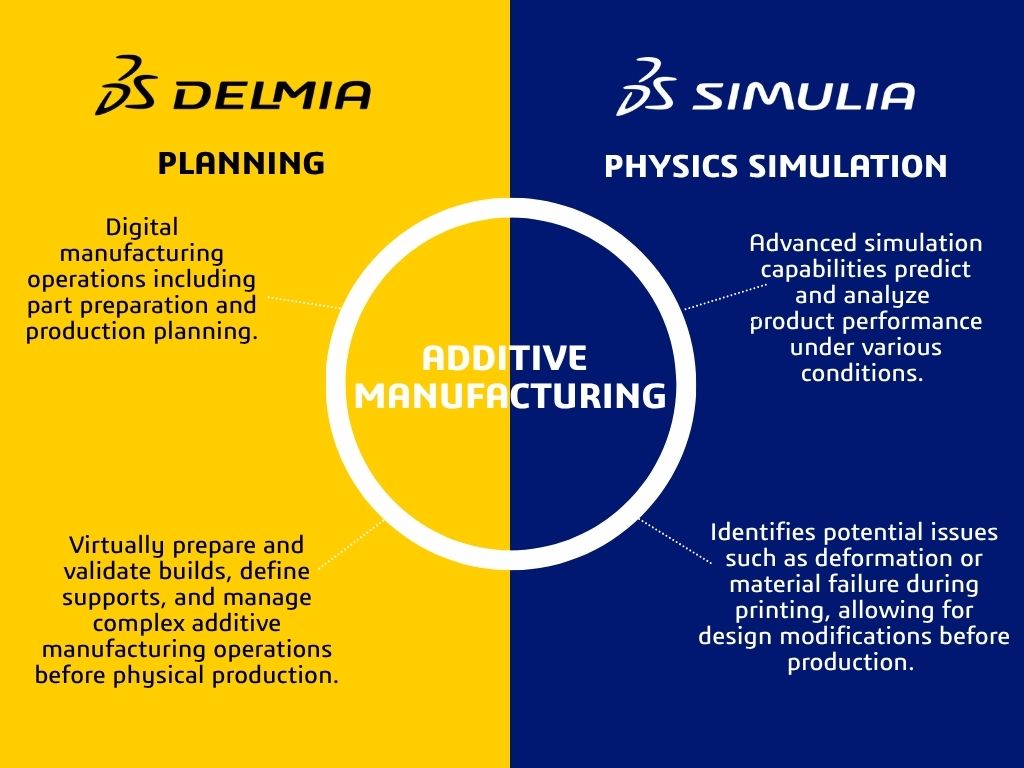
Dassault Systèmes offers a suite of tools that enhance manufacturing processes, particularly through SIMULIA and DELMIA. These two solutions complement each other rather than compete. SIMULIA provides advanced simulation capabilities that predict and analyze product performance under various conditions. It is instrumental in identifying potential issues such as deformation or material failure during printing, allowing for design modifications before production. DELMIA, on the other hand, focuses on digital manufacturing operations, including part preparation and production planning. Together, they form a continuous digital chain, integrating design, simulation, and manufacturing processes to enhance efficiency and reduce the need for manual intervention.
Primary Use Cases and Unified Workflow Advantages
The primary use cases for SIMULIA and DELMIA in additive manufacturing are distinct yet interconnected. DELMIA is primarily used for part preparation and defining machine operations, ensuring that components are printed accurately with the necessary support structures and orientations. SIMULIA evaluates the defined processes, predicting potential deformations and optimizing designs to prevent issues during production. The integration of these tools within a unified workflow eliminates the need to switch between different software, streamlining data management and process efficiency. This integration is a unique market offering, providing significant value to users by enhancing production efficiency and reducing time-to-market.
Unified Workflow Benefits
- Efficiency: Eliminates manual steps and data exchanges between different programs.
- Accuracy: Provides a single environment for design, simulation, and manufacturing.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces the risk of costly errors in production by simulating outcomes before physical manufacturing.
Additive Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
Additive manufacturing plays a crucial role in the Industry 4.0 paradigm, which emphasizes connectedness, the Internet of Things (IoT), and smart manufacturing processes. Within this framework, Dassault Systèmes provides tools that enable seamless integration from design to production. The 3DEXPERIENCE platform acts as a virtual twin of the physical product, allowing interactive simulations and real-time data collection from shop floors. This connectivity ensures that manufacturing processes are agile, adaptable, and capable of leveraging real-time insights to optimize operations.
Integration with Other Manufacturing Methods
Additive manufacturing can be effectively integrated with conventional manufacturing methods, such as robotics and machining, to enhance production capabilities. For instance, robotic systems are often used in material deposition techniques to print larger parts with complex geometries. Additionally, machining is frequently employed post-printing to achieve precision in final components. This hybrid approach, where additive manufacturing is combined with traditional methods, is gaining traction for its ability to produce high-precision parts efficiently.
Types of Additive Manufacturing Technologies and Supported Materials
The landscape of additive manufacturing is diverse, encompassing various technologies such as powder bed fusion, directed energy deposition, material extrusion, and electron beam melting. Each technology has its advantages and is suited for different applications:
- Powder Bed Fusion: Ideal for creating detailed and complex metal parts.
- Directed Energy Deposition: Used in aerospace for large-scale parts.
- Material Extrusion: Common in consumer-level 3D printing for plastics.
- Electron Beam Melting: Suitable for high-value metal components.
Dassault Systèmes’ tools support a wide range of materials, including metals, polymers, ceramics, and composites. This versatility allows manufacturers to choose the best material for their specific application, whether it’s lightweight polymers for consumer goods or robust metals for aerospace components.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Additive manufacturing excels in producing complex parts that are challenging to manufacture using conventional methods, offering unique design opportunities that are otherwise unattainable. The boundaries of what’s possible in manufacturing are expanded through our solutions in additive manufacturing. By integrating tools like SIMULIA and DELMIA into a cohesive workflow, we provide a powerful platform that supports the entire product lifecycle, from design to production. As the industry moves further into the era of Industry 4.0, the role of additive manufacturing in creating sustainable, efficient, and innovative products will only grow. Future developments in this field promise to enhance capabilities, offering even greater precision, material options, and integration with other manufacturing processes, thus empowering businesses to innovate and excel in a competitive marketplace.