MBSE as the Backbone of Digital Mission Engineering, Powered by AI

Firas Mahmoud, Asia-Pacific Senior Technical Sales Manager, Dassault Systèmes

Habibi Husain Arifin, Asia-Pacific South Industry Process Consultant, Digital Engineering Leader, Dassault Systèmes
Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) is the backbone for designing sophisticated, multi-domain and mission-critical systems. MBSE provides a systematic approach to achieve traceability and rigor from the early requirements engineering phase through architecture, design, implementation, and operation to the sustainment phase. However, the growth in complexity of defence, aerospace, automotive and autonomous systems has led to the explosion of documentation volumes and complexity that is no longer manageable with traditional manual approaches.
Organizations capture system specifications, regulations, contracts, standards, and stakeholder needs in complex, large document sets. This process makes manual requirements extraction, review, and traceability slow, error-prone and inconsistent across teams. Classical LLM-only approaches are highly black box AI-based and hallucination-prone for mission-critical applications. Engineering processes need to be deterministic, explainable, and auditable.
This creates the need for AI-augmented MBSE that uses NLP for robust linguistic analysis, ontologies for enforcing engineering logic and regulatory discipline, and GenAI for pattern recognition and architecture-pattern suggestion. MBSE also preserves end-to-end explainability and traceability from documentation to system architecture’s formalized specifications such SysML.
Dassault Systèmes 3DEXPERIENCE Platform manages these challenges with the NETVIBES Data Science Experience and CATIA Cyber Systems portfolio (CATIA Magic or also known as Cameo/MagicDraw). Together they provide document intelligence, automated requirements extraction, and NLP and ontology-driven quality and compliance checks. They also provide AI-assisted pattern generation for requirements and system architectures. The system captures outputs as structured SysML elements with cross-cutting relationships, supported by multi-agent, explainable workflows. This process keeps a human-in-the-loop approach and an Authoritative Source of Truth (ASOT) for mission-critical systems.
AI4RE: AI for Requirements Engineering

AI technologies are particularly well suited to address the bottlenecks created by unstructured and semi-structured documentation.
MBSE depends on clarity, traceability and accuracy. Yet, engineers often need to manually extract requirements from dense PDFs, technical manuals and specifications, an effort that is slow, error-prone and susceptible to misinterpretation.
One of the most impactful applications of AI in MBSE is the ability to transform extensive unstructured or semi-structured documents into organized, high-quality engineering insights.
While LLMs offer powerful generative capabilities, their inherent tendency to hallucinate and produce unverifiable statements makes them unsuitable as the primary mechanism for requirements extraction in MBSE. Engineering documentation requires deterministic, explainable, and traceable processing.
This is where Natural Language Processing (NLP) plays a significant role. NLP provides proven and reliable linguistic analysis through sentence detection, classification, terminology normalization and pattern recognition.
Systems can scan large document sets, detect requirements-like sentences and extract, analyze and classify them to deliver content into a structured requirements repository by combining NLP with targeted AI automation.
Dassault Systèmes 3DEXPERIENCE Platform, powered by NETVIBES Data Science Experiences and CATIA Cyber Systems Technology (including CATIA Magic/Cameo), enhances this workflow by enriching extracted requirements with metadata, semantic tags and full traceability links.
This foundation ensures downstream MBSE activities start with clean, structured, and context-aware requirements data.
AI4MBSE: Advancing Requirements Analysis and Engineering

A high-value application area of AI in MBSE is the analysis, refinement and validation of requirements. Traditionally, requirement elicitation and improvement required multiple review cycles and significant domain expertise.
AI shifts this paradigm by acting as an intelligent collaborator.
- NLP performs extraction, classification and linguistic normalization
- Ontologies enforce engineering discipline and prevent semantic drift
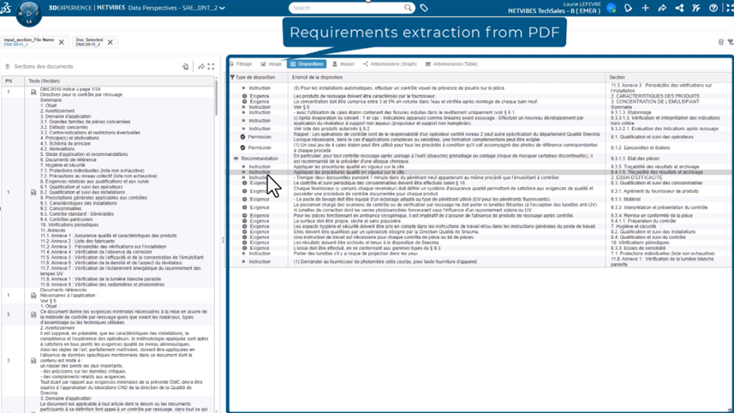
NLP improves requirements engineering by identifying linguistic structures, detecting requirements-like phrasing, normalizing terminology and mapping diverse wording styles to consistent categories.
It can identify ambiguity, flag incomplete or non-verifiable requirements, and evaluate quality at scale. For example, a vague requirement such as “the system shall be user-friendly” can be instantly flagged as non-measurable that is to be rewritten with objective, verifiable criteria.
The integration of ontologies further strengthens this process. Ontologies formalize engineering concepts, relationships and constraints, ensuring that NLP outputs, and when appropriate, generative insights, remain aligned with system architecture principles and engineering logic.
This alignment is particularly crucial for safety-critical domains, where any misinterpretation or inconsistency could compromise system integrity and compliance.
Evaluating requirement quality consistently and at scale raises documentation standards and accelerates system readiness.
AI4MBSE Sharpens Compliance, Regulation and Requirement Verification

Compliance is a cornerstone of systems engineering, especially in regulated sectors such as aerospace, automotive and defense.
AI enhances compliance and requirement verification in several important ways.
- NLP extracts, interprets and categorizes requirements
- AI applies rule-based checks and semantic validation libraries, comparing requirements against INCOSE’s best-practice guidelines and domain-specific industry standards
- Ontologies enforce alignment with engineering rules and regulatory constraints
This significantly reduces the time required for requirement audits, enables earlier detection of quality and compliance gaps, and improves verification planning, modeling readiness and certification efficiency.
AI for Generating System Architecture Patterns and Suggesting Requirements Traceability
AI is not a magic button that designs system architecture. Used properly, it becomes a disciplined pattern engine sitting on top of the MBSE framework and methodologies. This pattern engine recognizes structures, behaviors, and parameters from previous architectures, and captures patterns from unstructured documents. It then suggests structured patterns for both requirements and system architecture that engineers can use and trace back to source stakeholder needs.
AI is not a magic button, especially for mission-critical systems also. Any AI application in these systems must be tightly tailored to the mission engineering context, MBSE frameworks, methodologies, and formalized or semi-formalized specifications.
Requirements Pattern Recognition and System Architecture Pattern Generation using GenAI

Today, most mission-critical programs still start with a large and complex set of documents: regulations, contracts, specifications, and organizational standards. Teams then spend weeks or months manually reading, analyzing, classifying, and turning all of that into requirements and high-level designs. This process is slow, expensive, and does not scale as the document volumes grow. The three trending AI approaches to automate parts of these processes are using NLP, Ontology, and LLMs, respectively.
NLP and neural-network family AI such as LLMs, recognize the patterns in the documents, separate requirement structure from textual requirement, and categorize them into domain or category-specific classes through analysis. Teams can then use ontologies as the guardrails for these patterns to perform certain basic quality checks, such as building an ontological constraint based on INCOSE Guide to Writing Requirements.
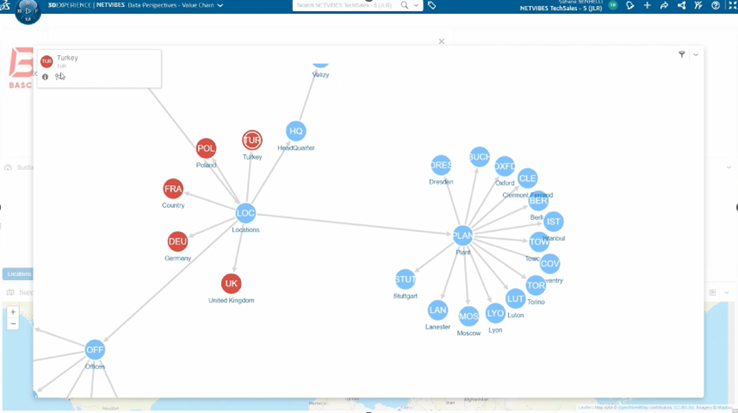
How do the three pillars of MBSE (methodologies, tools, and languages) become the critical factors for better output quality? Teams in organizations can tailor the AI application context with formalized metamodels or digital specifications such as SysML/UML tools like CATIA Magic (also known as Cameo/MagicDraw) and Netvibes on the 3DEXPERIENCE Platform using methodologies like Dassault Systèmes’ Cyber MagicGrid. The combination of these powerful configurations help structure the natural language artifacts into systematic models, such as systems decomposition and taxonomy, systems behaviors, and systems parameters, including their cross-cutting relationships. Capture and reuse of this systematic approach provides feedback for the next pattern generation.
Overcoming Requirement Explainability and Traceability Challenges

The systematic approach turns AI such as LLM from “a theoretical chatbot engine” into “a practical engine” that digs into the content of past and current documents, recognizes requirement patterns, and generates SysML-aligned architecture patterns. Defense organizations can then apply these patterns across different applications in tools such as CATIA Magic so that everyone works from the same structured Authoritative Source of Truth (ASOT).
In mission-critical systems, proofing the benefits of black-box AI can be very challenging. Every suggestion or recommendation must be explainable and traceable, so that business can capture AI-generated requirements, systems, functions and parameters as structured SysML elements. This ensures that the capture of these elements is not just done in natural language.
A multi-agent approach can make it clear which agent, prompt and rules produced which output. The whole pipeline – from document parsing to prompt building, semantic mapping of the outputs, and human review – is from the start visible, auditable, and traceable by design . This means the solution also suggests links between requirements, systems and functions.
Keeping requirements traceable in AI-generated system architectures is the most crucial factor, and it is difficult to achieve without explainability and human-in-the-loop involvement.
Looking Ahead: GenAI, NLP, and Ontologies as the Next Evolution of MBSE
The future of MBSE will be shaped by the combined strengths of:
- NLP for linguistic understanding and structured extraction
- Generative AI for contextual reasoning and intelligent automation
- Ontologies for engineering logic and semantic discipline
- Data Science for data intelligence, traceability and knowledge continuity

Together, these technologies empower engineering teams to move from document-centric workflows to knowledge-centric MBSE, reducing manual effort, enhancing requirement quality, and accelerating architecture development.
Dassault Systèmes provides precisely the solutions and expertise that help defense and aerospace organizations reduce manual effort, enhance requirement quality, and accelerate architecture development. As system complexity continues to grow, AI-enabled MBSE will empower engineers to focus on what truly matters: designing safe, innovative, and mission-ready systems.

